Running a multilingual WordPress site with WPML can be powerful, but it is also complex. Based on real support cases from the WPML support forum, users repeatedly encounter similar problems across page builders, custom fields, translations, SEO, performance, language routing, and more.
This guide will explain those issues step-by-step, so you can recognize symptoms early, understand what’s actually happening behind the scenes, and apply proven fixes that have worked for other users.
1. Page Builder Settings Sync Across Languages (Elementor / WPBakery)
Detection:
- Editing a page in one language automatically changes the content or settings in another language.
- Custom fields inside Elementor widgets display the same value across languages.
- WPBakery pages can only be edited in the default language when WPML is active.
Causes:
WPML synchronizes page builder data by default to maintain consistency between translations. In builders like Elementor and WPBakery:
- Widget configurations are often shared between languages.
- Custom fields inside widgets are not treated as language-specific unless explicitly translated.
- WPML’s Translation Editor overrides the page builder’s native editing behavior.
Solution:
- Switch the affected page or template to manual translation mode.
- Edit each language version directly using the page builder.
- Avoid using the Translation Editor for pages built with complex widgets.
- Re-save both the original and translated versions after changes.
2. Custom Fields Not Translating or Displaying Inconsistently (ACF)
Detection:
- ACF fields appear in the translation editor but not on the frontend.
- Fields translate correctly in one language but not in another.
- Old values continue to appear after updating translations.
- Some fields are completely missing in certain languages.
Causes:
- Incorrect translation preferences (copy, copy once, translate).
- Use of “Expert mode” without consistent configuration.
- Duplicate field names (e.g., title, description) across field groups.
- Translation jobs completed but not delivered.
- Cached frontend output masking updated translations.
Solution:
- Ensure all ACF field names are unique across the site.
- Use recommended translation preferences before switching to Expert mode.
- Re-save the original page, then update the translation.
- Clear all cache layers (plugin, server, CDN).
- Check WPML Translation Editor error logs for delivery issues.
3. Translated Pages Redirect or Don’t Load Correctly
Detection:
- Translated pages redirect to the default language.
- Homepage translation loads the wrong URL.
- Translation icons switch between plus, pencil, and circular arrows.
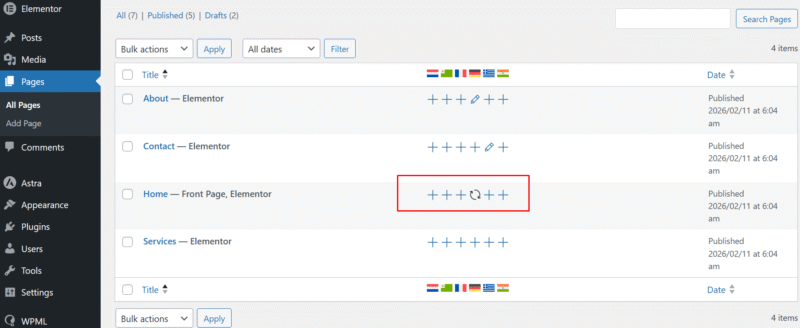
- Pages appear translated, but are inaccessible.
Causes:
- Translation jobs are stuck or assigned to another user.
- Translations are marked as completed but not delivered.
- Multiple editors (manual and Translation Editor) are used inconsistently.
- URL routing depends on translation completion status
Solution:
- Go to WPML > Translation Management.
- Cancel any stuck or unfinished translation jobs.
- Reopen and complete the translation.
- Confirm the translation status is published and delivered.
- Several users resolved homepage redirect issues simply by canceling and re-creating the translation job.
4. Broken URLs
Detection:
- Language URLs lead to “Page not found” errors.
- Switching languages results in incorrect domain or subdirectory URLs.
- Translated pages load without images or broken layouts.
Causes:
- WordPress rewrite rules are not refreshed automatically.
- Existing translations still point to old URL structures.
- Cached data inside WPML and WordPress persists after migration.
Solution:
- Go to Settings > Permalinks and click Save Changes.
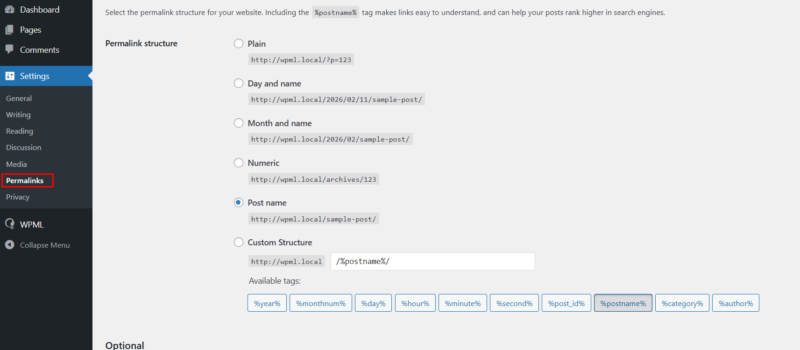
- Clear WPML caches under WPML > Support > Troubleshooting.
- Re-save affected translations.
- Clear the site and server caches.
5. Search Filters and Dynamic Content Not Working in Translated Pages
Detection:
- Price filters or dropdowns work only in the default language.
- Translated pages show empty or hidden options.
- String translations exist but do not appear on the frontend.
Causes:
From the dataset, this typically occurs when:
- Themes or widgets conditionally hide elements based on language.
- JavaScript logic is not language-aware.
- Translated values exist, but are wrapped in hidden containers.
- Plugin compatibility is incomplete.
Solution:
- Inspect frontend HTML to confirm whether values are present but hidden.
- Temporarily deactivate WPML (after backup) to confirm the source of the issue.
- Test in a minimal plugin setup.
- Escalate to the theme or plugin authors if the logic is language-dependent.
6. SEO Issues with Browser Language Redirect
Detection:
- SEO tools report hreflang or language mismatches.
- Issues disappear when browser language redirect is disabled.
Causes:
WPML’s browser-based language redirect changes content delivery depending on visitor settings. This can:
- Serve different content to crawlers than to users.
- Trigger indexing warnings in SEO audit tools.
Solution:
- Disable browser language redirect if SEO consistency is required.
- Use static language URLs instead.
- Follow WPML documentation regarding indexing behavior.
7. WPML Activation Causes Site Crashes or Admin Errors
Detection:
- Activating WPML crashes the site.
- The translation dashboard becomes inaccessible.
- Saving large pages causes 503 errors.
- Debug logs show no clear WPML errors.
Causes:
Resolved cases point to:
- Server memory exhaustion.
- Low execution time limits.
- Heavy ACF synchronization.
- Hosting-level request rejection.
Solution:
- Increase PHP memory limits.
- Increase max_execution_time.
- Disable heavy ACF synchronization where possible.
- Test with minimal plugins enabled.
- Contact the hosting provider to review server logs.
Final Thoughts
WPML is a feature-rich multilingual plugin, but many issues arise from hidden translation states, page builder synchronization, custom field misconfiguration, or URL and cache dependencies.
Understanding how WPML handles translations internally makes troubleshooting far easier and prevents recurring problems.